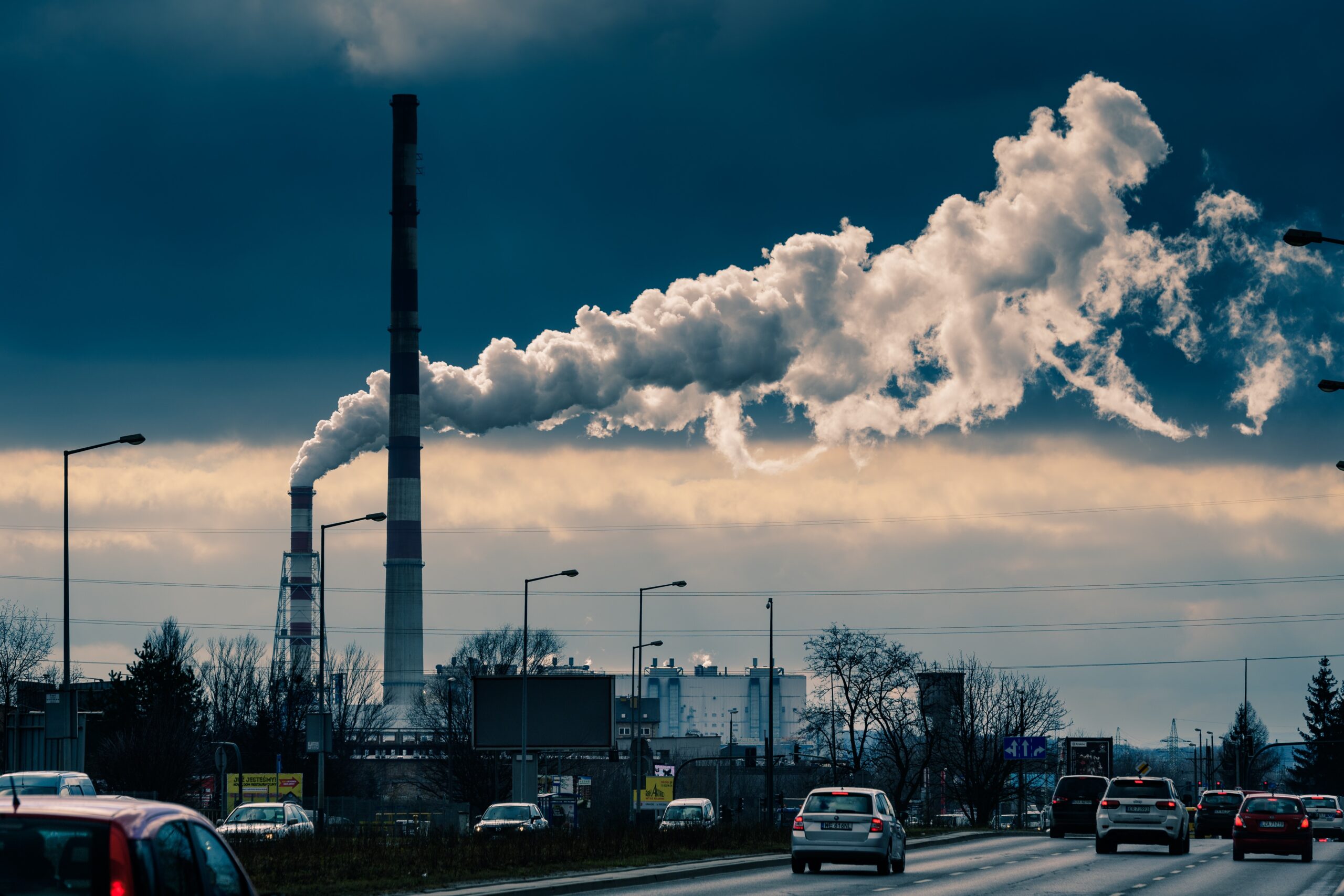
Polluted air has a higher toll than you might imagine. According to the Environmental Defense Fund, “air pollution is now the biggest environmental risk for early death, responsible for more than 6 million premature deaths each year.”
Let’s explore how air pollution is defined, its causes and consequences, and how you can help promote clean air in your community.
What is air pollution?
Air pollution is defined by the WHO as “contamination of the indoor or outdoor environment by any chemical, physical, or biological agent that modifies the natural characteristics of the atmosphere.” Air pollution examples include pollutants like:
- Particulate matter
- Carbon monoxide
- Ozone
- Nitrogen dioxide
- Sulfur dioxide
These types of air pollution affect air quality, which is measured by the Air Quality Index or AQI. AQI values run from 0 to 500, with AQI values over 300 representing hazardous air quality.
What Causes Air Pollution?
Air pollution is caused by a wide range of factors, both natural and human-made. Natural sources of air pollution include volcanic eruptions, wildfires, and dust storms. However, the majority of air pollution is caused by human activities such as transportation, industrial processes, and energy production. For example, the burning of fossil fuels such as coal, oil, and gas releases pollutants such as carbon monoxide, nitrogen oxides, and sulfur dioxide into the air. Other common causes of air pollution include:
- Vehicle emissions
- Manufacturing
- Mining
- Agriculture
The pollutants from these and other sources can also have a greater impact when combined with certain weather conditions. Here in Colorado, the summer heat often interacts with oil and gas emissions to produce harmful ground-level ozone, while increased wildfires trap pollutants and add to particulate matter.
Air Pollution Effects
Air pollution has a range of negative effects on both human health and the environment. For humans, long-term exposure has been linked to chronic health conditions, and even short-term exposure to high levels of air pollution can cause:
- Respiratory problems (coughing, wheezing, and shortness of breath)
- Headaches
- Nausea
- Dizziness
The National Parks Conservation Association reports that “each summer, kids in Colorado suffer an estimated 32,000 asthma attacks linked to the oil and gas industry’s smog pollution.”
The environmental effects of air pollution include health risks for various species and ecosystem damage due to resulting processes like acid rain. Additionally, the burning of fossil fuels releases greenhouse gasses into the atmosphere, contributing to climate change and its devastating impacts.
Air Pollution Solutions
Reducing air pollution requires a multifaceted approach that addresses the sources of emissions across various sectors. Advocating for policy changes, introducing emissions standards, and reducing waste are all key parts of the solution. You can also make individual choices that impact air pollution, such as opting for public transportation, walking, or cycling. Finally, one of the most effective ways to help is to shift away from fossil fuels and toward renewable energy sources such as wind and solar power.
Want to promote access to clean energy in your community? Join your fellow Coloradoans making the switch to renewable energy. Here at the Colorado Clean Energy Fund, we support Coloradoans in their efforts to transition to clean energy. We use the tools we have as a green bank to break down the financial barriers that inhibit access to clean energy for communities across the state. Explore our products and programs here to see how we can help you.
Sources:
- https://www.edf.org/health/effects-of-air-pollution
- https://www.who.int/health-topics/air-pollution#tab=tab_1
- https://www.airnow.gov/aqi/aqi-basics/
- https://education.nationalgeographic.org/resource/air-pollution/
- https://conservationco.org/2022/03/25/five-reasons-colorados-air-quality-is-so-bad/
- https://www.nrdc.org/stories/air-pollution-everything-you-need-know#effects
- https://www.npca.org/advocacy/91-air-pollution-in-colorado-our-lives-and-parks-at-risk